June 2022
·
19 Reads
·
2 Citations
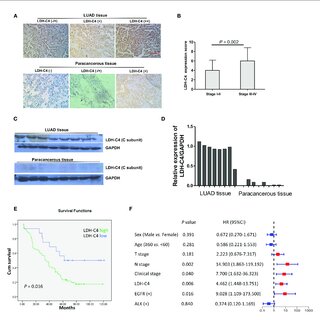
Objective As a cancer-testis antigen (CTA), human lactate dehydrogenase C4 (LDH-C4) enzyme protein encoded by the LDHC gene has been reported to be involved in the occurrence and development of various malignancies, while its expression and clinical significance in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) remain unclear. This study aims to investigate the expression of LDH-C4 in LUAD and its diagnostic and prognostic value.Methods The mRNA and protein levels of LDH-C4 in LUAD and adjacent normal tissues were analyzed based on the UALCAN database, and the prognostic significance was assessed using the LOGpc database. The LDHC mRNA level in serum and serum secretion of LUAD patients was determined by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Based on the high-throughput LUAD tissue chip combined with immunohistochemistry (IHC), the protein level of LDH-C4 in LUAD tissues was measured, and its correlation with clinicopathological features and prognosis was analyzed.ResultsLDHC expression was upregulated in LUAD, which was related to the clinical stage and poor prognosis of patients. The positive rates of LDHC mRNA expression in serum and exosome of LUAD patients were 78.3% and 66.7%, respectively. The area under the curve (AUC) of serum and exosomal LDHC in the diagnosis of LUAD was 0.8121 and 0.8925, respectively. The expression of LDHC in serum and serum-derived exosomes from LUAD patients was negatively correlated with medical treatment and positively correlated with the recurrence of LUAD. The positive expression rate of LDH-C4 in LUAD tissues was 96.7% (89/92), which was significantly higher than that in adjacent normal tissues 22.6% (19/84) (p < 0.001). The median overall survival (OS) time of patients with a high expression of LDH-C4 was significantly shorter than that of patients with low expression (34 months versus 62 months) (p = 0.016). Further relative risk analysis exhibited that the expression of LDH-C4 was an independent prognostic factor of OS in patients with LUAD.ConclusionsLDHC/LDH-C4 expression was upregulated in LUAD, and LDH-C4 could be used as a molecular indicator of the prognosis of LUAD. Serum and serum-derived exosomes of LDHC can be used as an important biomarker for the diagnosis, efficacy evaluation, and recurrence monitoring of LUAD.